– As of October 2017, there were 31,316 Oncology Certified Nurses
– If you’re an ONS/APHON Member, the fee to take the OCN exam is $296. If you’re a nonmember, the fee to take the exam is $416.
Being an oncology nurse can make a difference in a lot of people’s lives-you help those who are diagnosed with cancer. Oncology nurses care for people of all ages while supporting the patient and their family, and being a caregiver through the stress of their diagnosis and treatment of cancer. They are also responsible for assisting in cancer therapy, administering medication, and maintaining patient records.
OCN Eligibility

• A current and active RN license
• A minimum of 2 years/24 months of practice as an RN in the past 4 years/48 months prior to submitting your application.
• A minimum of 2,000 hours of specialty nursing practice in the past 4 years/48 months prior to submitting your application:
– Adult Oncology Nursing Practice for OCN
– Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Nursing practice for CPHON
– Breast Care Nursing practice for CBCN
– Blood and Marrow Transplant Nursing practice for BMTCN
• A minimum of 10 contact hours of credential-specific continuing nursing education or an academic elective completed in the three years/36 months prior to submitting your application.
OCN Certification Practice Test
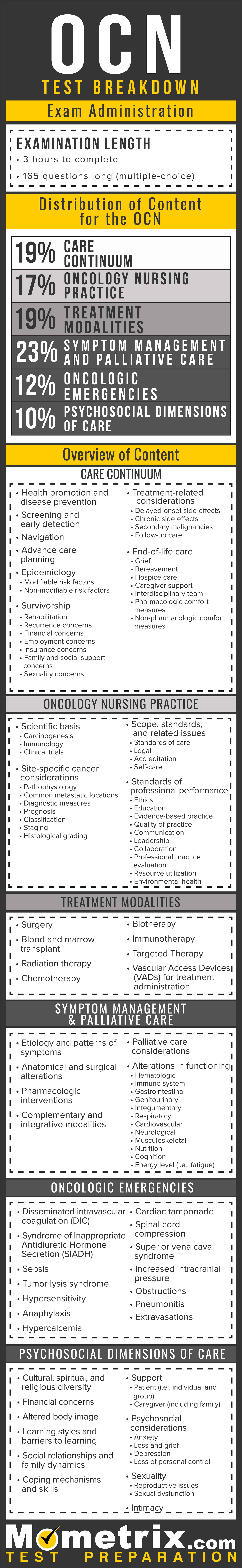
The Oncology Certified Nurse Certification certifies current RNs to work in the oncology area of nursing. The OCN exam is offered most of the year. The certification exam contains 165 multiple-choice questions that need to be completed within 3 hours.

The OCN exam includes six major subject areas:
- Care Continuum
- Oncology Nursing Practice
- Treatment Modalities
- Symptom Management and Palliative Care
- Oncologic Emergencies
- Psychosocial Dimensions of Care
OCN Certification Exam Prep Course
- Care Continuum
- Health promotion and disease prevention (High-risk behaviors, preventive health practices)
- Screening and early detection
- Navigation
- Advance Care Planning (advance directives)
- Epidemiology
- Modifiable risk factors (smoking, diet, exercise, occupation)
- Non-modifiable risk factors (age, gender, genetics)
- Survivorship
- Rehabilitation
- Recurrence concerns
- Financial concerns
- Employment concerns
- Insurance concerns
- Family and social support concerns
- Sexuality concerns
- Treatment-related consideration
- Delayed-onset side effects
- Chronic side effects
- Secondary Malignancies
- Follow-up care
- End-of-life care
- Grief
- Bereavement
- Hospice care
- Caregiver Support
- Interdisciplinary team
- Pharmacologic comfort measures
- Non-pharmacologic comfort measures
- Oncology Nursing Practice
- Scientific basis
- Carcinogenesis
- Immunology
- Clinical trials (research protocols)
- Site-specific cancer considerations
- Pathophysiology
- Common metastatic locations
- Diagnosis measures
- Prognosis
- Classification
- Staging
- Histological grading
- Scope, standards, and related issues
- Standards of care (nursing process)
- Legal (including documentation)
- Accreditation (The Joint Commission)
- Self-care (managing compassion fatigue)
- Standards of professional performance
- Ethics (patient advocacy)
- Education
- Evidence-based practice (Putting Evidence Into Practice (PEP) guidelines and research)
- Quality of practice
- Communication
- Leadership
- Collaboration
- Professional practice evaluation
- Resource utilization
- Environmental health (safety, personal protective equipment, safe handling)
- Scientific basis
- Treatment Modalities
- Surgery
- Blood and marrow transplant
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Biotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- Vascular Access Devices (VADs) for treatment administration
- Targeted Therapy
- Symptom Management and Palliative Care
- Etiology and patterns of symptoms (acute, chronic, late)
- Anatomical and surgical alterations (lymphedema, ostomy, site-specific radiation)
- Pharmacology interventions
- Complementary and integrative modalities (massage, acupuncture, herbal supplements)
- Palliative care considerations
- Alterations in functioning
- Hematologic
- Immune System
- Gastrointestinal
- Genitourinary
- Integumentary
- Respiratory
- Cardiovascular
- Neurological
- Musculoskeletal
- Nutrition
- Cognition
- Energy level (fatigue)
- Oncologic Emergencies
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH)
- Sepsis (including septic shock)
- Tumor lysis syndrome
- Hypersensitivity
- Anaphylaxis
- Cardiac tamponade
- Spinal cord compression
- Superior vena cava syndrome
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Obstructions (bowel and urinary)
- Pneumonitis
- Extravasations
- Psychosocial Dimensions of Care
- Cultural, spiritual, and religious diversity
- Financial concerns (including available resources)
- Altered body image
- Learning styles and barriers to learning
- Social relationships and family dynamics
- Coping mechanisms and skills
- Support
- Patient (individual and group)
- Caregiver (including family)
- Psychosocial considerations
- Anxiety
- Loss and grief
- Depression
- Loss of personal control
- Sexuality
- Reproductive issues (contraception, fertility)
- Sexual dysfunction (physical and psychological effects)
- Intimacy
OCN Scores
Each of the ONCC exams are scored using a scaled score system. A scaled score of 55 is the passing score for all ONCC exams. However, the scaled score of 55 translates into a different raw score on different exams.
OCN FAQ
What is the OCN exam?
The OCN exam is the Oncology Certified Nurse certification exam. This exam measures the candidate’s knowledge and skills that are needed to become an OCN.
How many questions are on the OCN exam?
There are 165 multiple-choice questions on the OCN exam.
How long do you have to take the OCN test?
You are given 3 hours to complete the OCN exam.
What is a passing score for the OCN exam?
A passing score for the OCN test is a scaled score of 55.
What if I failed the OCN exam?
If you failed the OCN exam, you can immediately apply to retake the test within the 90-day window without having a waiting period. If you take the exam three times and do not pass, you will be required to wait a minimum of one year before retaking the exam.
How much does it cost to take the OCN test?
If you’re an ONS/APHON Member, the fee to take the OCN exam is $296. If you’re a nonmember, the fee to take the exam is $416

