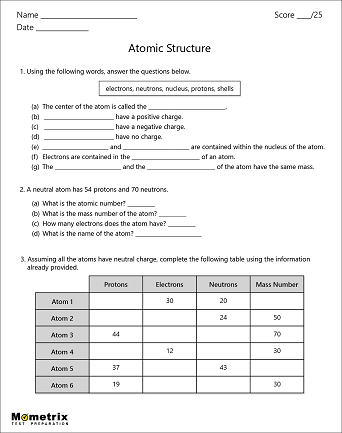
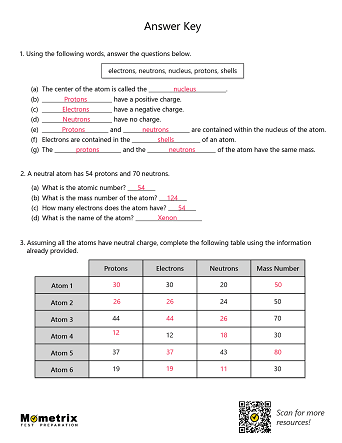
Atoms are the building blocks of the universe; they make up everything you see around you.
Atomic Structure
At the very center of an atom is the nucleus, which is made up of small particles called protons and neutrons. Protons are very small, positively-charged particles, and neutrons are neutral particles that have no charge.
Atoms can have just one proton or they can have multiple. A group of atoms that all have the exact same number of protons is called an element. For example, hydrogen is an element with one proton in the nucleus and carbon is an element with 6 protons.
Stable Atoms
In general, an atom will have a specific number of neutrons in the nucleus, meaning the atom won’t lose or gain any neutrons for a very long time. This is called a stable atom.
Usually, a stable atom has an equal number of neutrons and protons, but there are exceptions. To find the mass number of an element you add the number of protons and neutrons together, so protons + neutrons = mass number. This gives us names like Carbon-12 or Carbon-14, which are types of carbon atoms used in carbon dating!
Orbiting the atom’s positively charged center are particles with a negative charge called electrons. The electrons are attracted to the positive nucleus, but they can escape their orbit by an outside force.
Positive, Negative, and Neutral Charge
Atoms have a certain number of electrons orbiting the nucleus. If the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons, the overall electric charge of the atom is neutral. If the atom has more electrons than protons, its charge will be negative. With fewer electrons than protons, the atom will have a positive charge.
The electrons determine how atoms interact with each other. Atoms can share electrons to form molecules, which are particles made up of many atoms. Water is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. These three atoms share electrons.
Properties of Atoms
Now that we have talked about the different parts of the atom, let’s summarize a few properties of atoms. Atoms have an atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus. The periodic table arranges atoms in increasing atomic number. The charge of an atom is calculated based on the difference between the number of protons in the nucleus and the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Review
An atom is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons. The number of electrons will determine how atoms interact with one another and decide if the atom as a whole is positive, negative, or neutral. The mass number of an atom is found by adding together the number of protons and neutrons. And finally, the charge of an atom is determined by the number of protons and electrons in the atom.
Thank you so much for watching, and see you guys next time!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What is atomic structure?
A
Atomic structure refers to the structure of an atom; a positvely charged nucleus consisting of both protons and neutrons, surrounded by negatively charged electrons.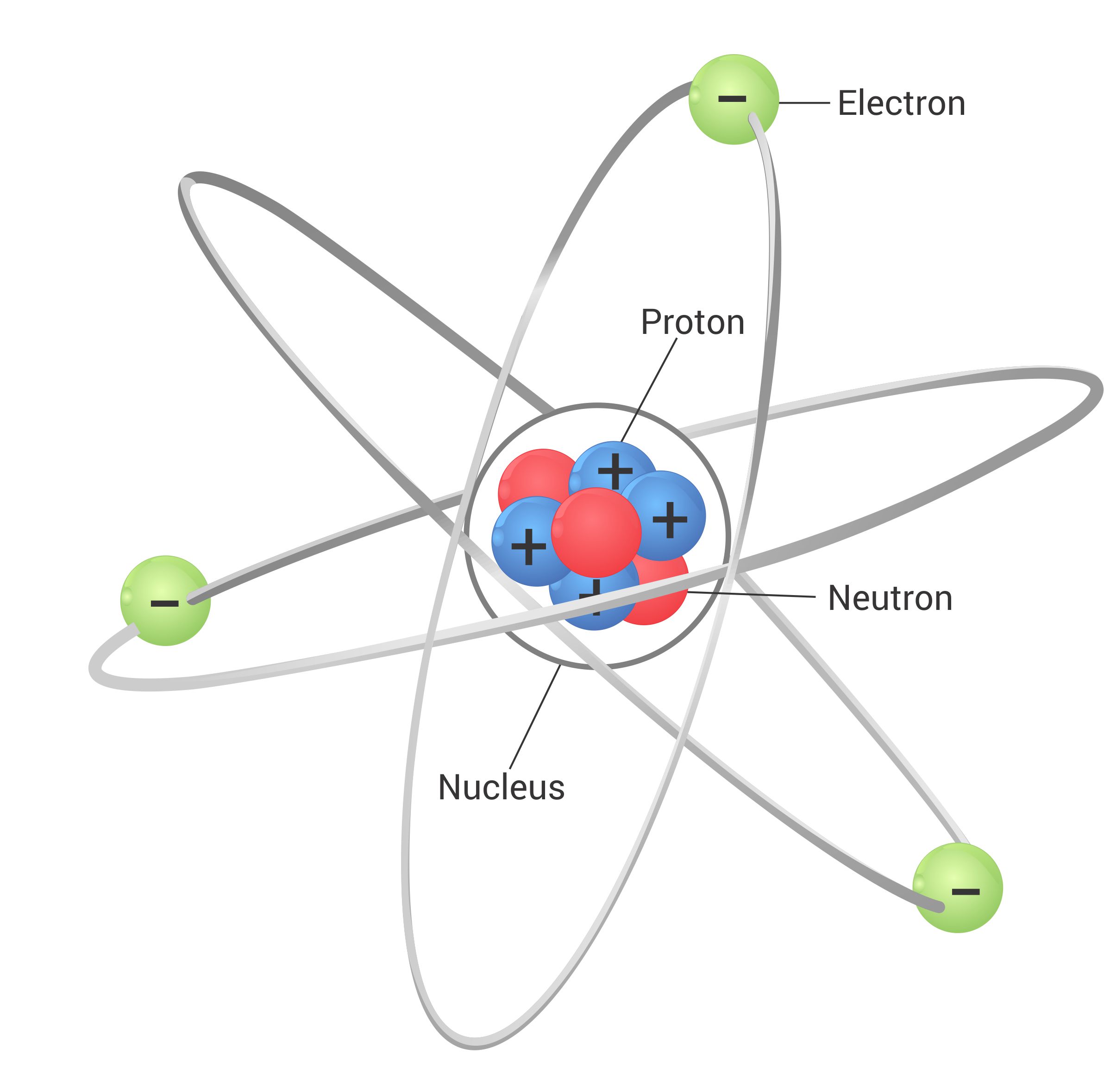
Q
What does the nucleus do?
A
The nucleus is the dense center of the atom that includes the atom’s neutrons and protons.
Q
How do you find the number of protons?
A
You can find the number of protons for an element by looking at the element’s atomic number on the periodic table. The atomic number represents the atom’s number of protons.
Q
How do you find the number of neutrons?
A
To find the number of neutrons an atom has, simply subtract the element’s atomic number from its mass number.
Q
How do you find the number of electrons?
A
The number of atoms in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons the atom contains.
Q
What makes a stable atom?
A
An atom is considered stable if the outermost shell is filled with electrons.