
Hey, guys! Welcome to this video on pH levels.
What is pH?
The pH value of a solution is a measure of its acidity. Most solutions have a pH value between 0 and 14 on the pH scale.
Solutions with a pH value of 7, at the middle of the pH scale, are called neutral. If a solution has a pH value smaller than 7, it’s called acidic. If the pH value is larger than 7, the solution is called basic or alkaline.
For instance, vinegar has a pH value of 2.4 and is acidic, pure water has a pH value of 7 and is neutral, and household bleach has a pH value of 13 and is basic.
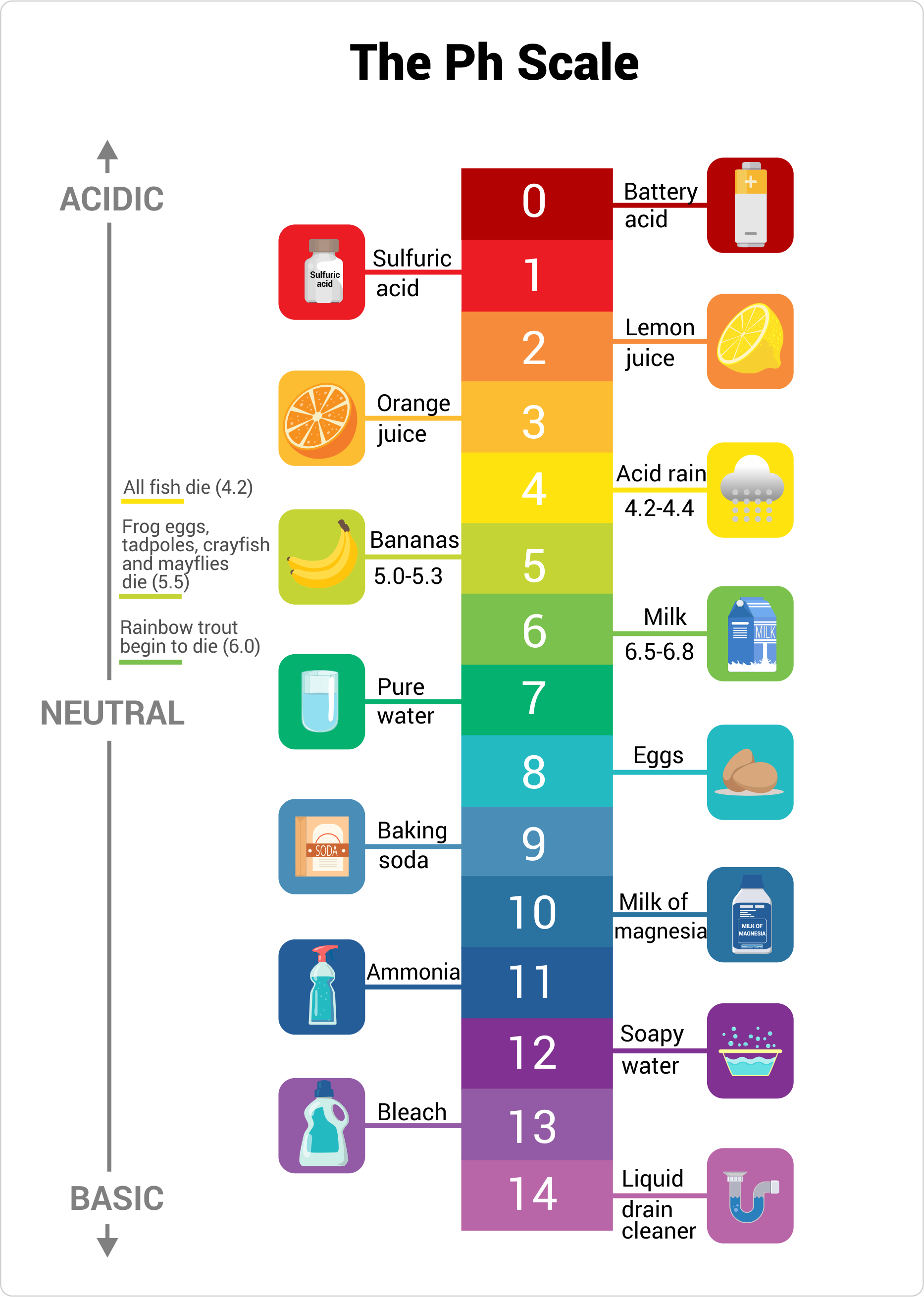
pH Acidity
Note a solution that is more acidic has a smaller pH value. That has to do with the definition of pH. Generally, the acidity of a solution is defined by the concentration of hydronium ions in it. The higher the concentration of hydronium ions, the more acidic the solution. For instance, a solution with a 0.5 M concentration of hydronium ions is more acidic than a solution with a 0.05 M concentration of hydronium ions.
Real-World Examples
Let’s look at a few common substances and where they fall on the pH scale.
- Battery acid, a very corrosive substance, is a strong acid, therefore it falls on the lower end of the pH scale with a pH of approximately 1.
- The gastric juices in your stomach, which help you to digest food, are acidic, too, with a pH value somewhere between 1.5 and 3.
- Lemon juice contains a citric acid and has a pH value of 2 to 3, just like vinegar.
- Most soft drinks are quite acidic with pH values between 2.5 and 4. This is one of the reasons dentists don’t want you to drink soft drinks: the acid in soft drinks dissolves the enamel of your teeth. Milk is a lot better for your teeth, with a pH of approximately 6.5.
- Rainwater is somewhat acidic, with a pH of approximately 5. However, industrial pollutants can make rainwater more acidic, with a pH value anywhere between 2 and 4, which can be damaging to plant life.
- Pure water is neutral with a pH of 7.
- Blood is slightly basic, with a pH value of 7.4.
- Seawater has a pH value of approximately 8.
- Solutions of baking soda are mildly basic with a pH value of 8.4, therefore baking soda is used to clean up small acid spills in chemistry labs.
- Soapy water has a pH value of 9 to 10, which helps to remove the grease from your skin or from dirty dishes.
- Just as strongly acidic solutions pose hazards, so does strongly basic solutions. Lye, oven cleaner, and household bleach have a pH value of approximately 13, so be careful around them.
Thanks for watching this overview of pH levels. See you guys next time!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What is pH?
A
pH is a measure of how acidic or basic an aqueous solution is based on the amount of hydrogen ions in the substance.
Q
What does pH stand for?
A
pH stands for “potential of hydrogen.”
Q
What is pH balance?
A
pH balance refers to the levels or ratio of acids and bases in your body at which your body functions best.
Q
What is the pH of water?
A
The pH of pure water is 7, which is considered neutral.
Q
How do you calculate pH?
A
To calculate a solution’s pH you must know the concentration (molarity) of hydronium ions (H3O+). From there you multiply -log10 by the molar hydrogen ion concentration.
Q
What does pH measure?
A
pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is based on its hydrogen ion content.
Q
What is a pH scale?
A
The pH scale is a range from 0 to 14 used to interpret the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. 7 is considered neutral, while values above 7 are basic and values below 7 are acidic.