
Hey guys, welcome to this Mometrix video on eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
In this video, we will take a look at what each is, and how they are different.
Eukaryotes
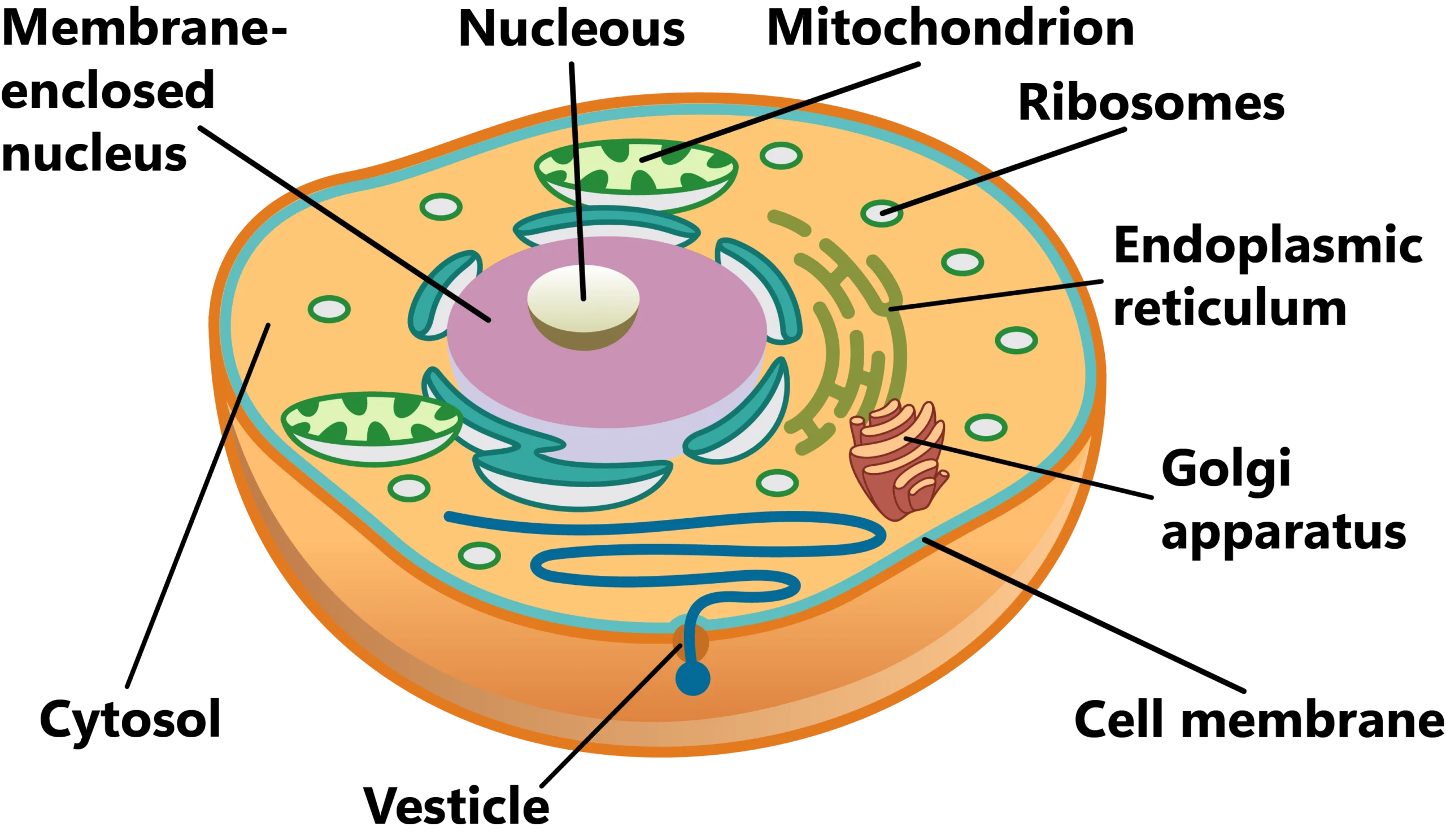
Eukaryotes can be defined as any organism that has a cell or cells that are complex; more specifically, they have a membrane-bound nucleus where all their genetic information is stored.
The nucleus is not the only organelle contained within a eukaryotic cell membrane, but a membrane-bound nucleus is unique to eukaryotes. All of the eukaryotic cell’s DNA is linear, and is stored within the nucleus. Eukaryotes can contain several other membrane-bound organelles, like a golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrion, and so on! Eukaryotic cells are large cells generally between 10-100 micrometers.
Examples of Eukaryotic Cells
Guess what? You are a eukaryote, and all the cells that make you up are eukaryotic.
Some other examples of eukaryotes include protists, fungi, plants, and animals.
Prokaryotes:
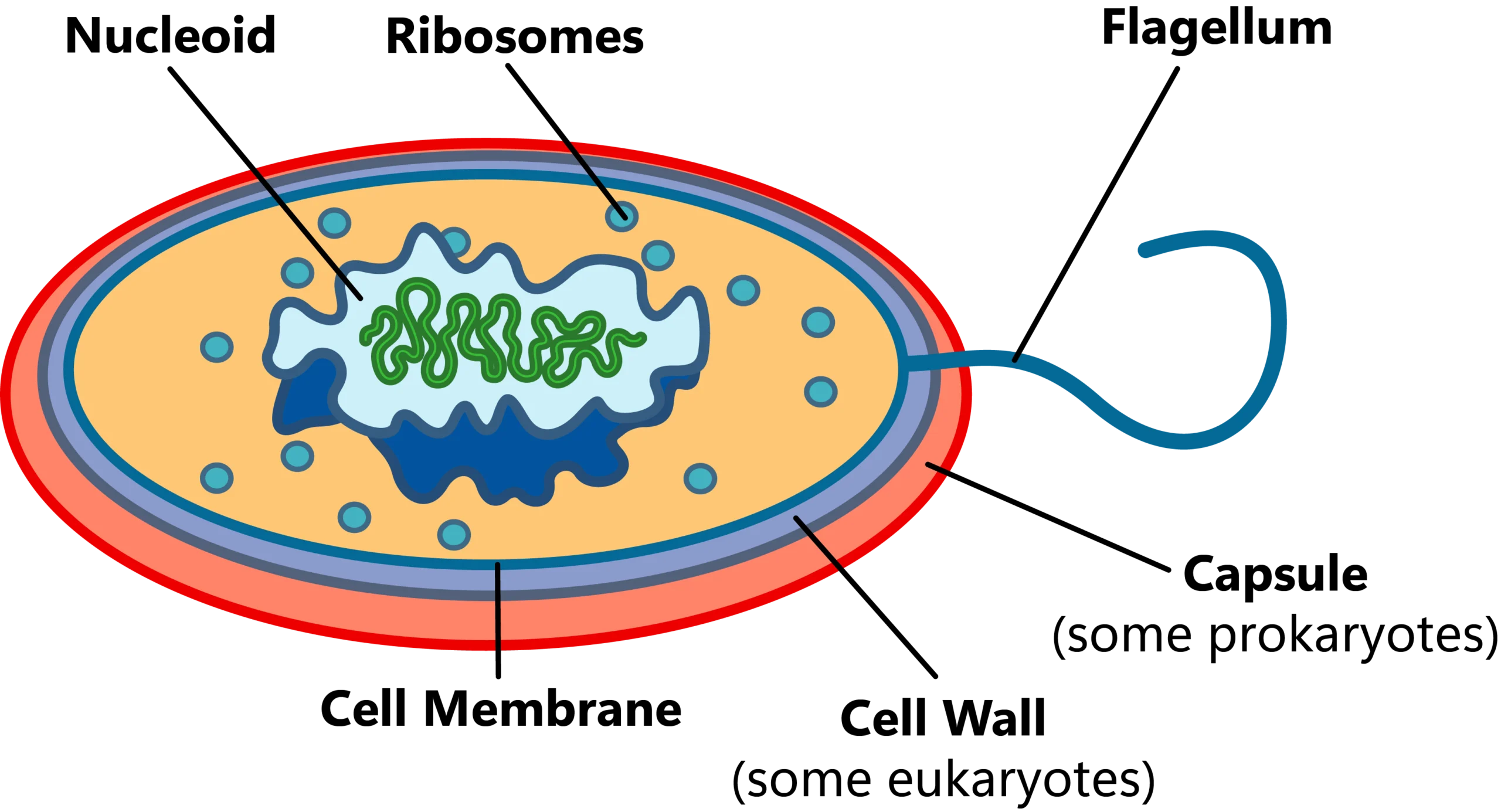
Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, are not quite as complex as eukaryotic cells. A prokaryote is a non-complex, single-celled organism that does not contain a nucleus, nor does it contain any membrane-bound organelles.
It’s important to note that eukaryotes can be unicellular as well, but a prokaryote will is always unicellular. All of a prokaryote’s DNA is circular and floats freely within the cytoplasm of the cell. Prokaryotes are much smaller than eukaryotes; they range in size from 1 to 5 micrometers.
Examples of Prokaryotes
Examples of prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea.
I hope that this overview was helpful for you. See you next time!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A
Prokaryotic cells are much simpler than eukaryotic cells as they are usually smaller, single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or any membrane-bound organelles.
Q
Where is the DNA located in a eukaryotic cell?
A
In eukaryotic cells, DNA is mostly contained in chromosomes within the nucleus, although there is some DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Q
Do eukaryotes have a cell wall?
A
Some eukaryotes have a cell wall, including plants, some fungi, and some protists. Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that do not contain a cell wall.
Q
Do prokaryotes have a cell wall?
A
Most prokaryotic cells have a rigid cell wall, but the composition of the cell wall differs between the Bacteria and Archaea domains.
Q
Do prokaryotic cells have a nucleus?
A
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and this is one of the characteristics that differentiates a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell.
Q
Do prokaryotic cells have DNA?
A
Prokaryotic cells do have DNA, but it is located in the center of cell in a region referred to as a nucleoid.
Q
Do prokaryotic cells have mitochondria?
A
Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles and thus do not have mitochondria.