Hey there! Welcome to this Mometrix video on DNA.
What is DNA?
DNA is the initialism for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is the organic chemical of complex molecular structure located in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as in many viruses.
DNA is what makes up the codes for genetic information of inherited traits to be transmitted. The way DNA is structured determines things like the hair length of a dog, the color of your eyes, facial structure, and even things like the effect of a virus on its host.
The Structure of DNA
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick discerned the double helix structure of DNA. The double helix consists of two DNA strands wound or twisted around each other in a sort of arrangement that looks like a spiraling staircase.
Each strand is made up of a long chain of monomer nucleotides (nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA).
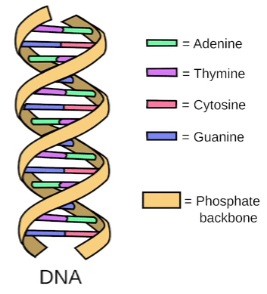
The nucleotide of DNA is made up of a deoxyribose sugar molecule, or a five-carbon sugar molecule, and attached to this sugar molecule is a phosphate group along with one of four nitrogenous bases. The bases consist of two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine).
Nucleotides are bound together by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next nucleotide. This bond forms a phosphate-sugar foundation from where the nitrogenous bases project.
The strands are held together by a hydrogen bond between the bases. Sequencing of this bonding is very particular: The purine adenine bonds only with the pyrimidine thymine, and the pyrimidine cytosine only bonds with the purine guanine.
Because of this highly stable configuration of the DNA molecule, it allows the DNA molecule to act as a template for the replication of a new DNA molecule, but also for the transcription of the related RNA molecule. A segment of DNA that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a particular protein is called a gene.
DNA Replication
So the way the DNA replicates is by separating back into two single strands.
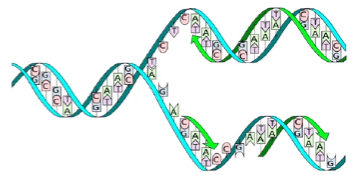
These two, now separated, strands are what act as the template for that replication to take place. The new strands are copied by the same principle of hydrogen-bond pairing between bases that make up the double helix. Once the two strands break apart, and replicate, by bonding to another strand, each new DNA molecule contains one strand of the original. This is often referred to as semiconservative replication, and it is key to the stable inheritance of genetic traits.
Within a cell, DNA ordered into dense protein-DNA complexes are called chromosomes. Inside of eukaryotes, you can locate the chromosomes inside the nucleus. However, DNA can also be found in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA.
In prokaryotes, all the DNA is a single round-shaped chromosome in the cytoplasm. There are a few prokaryotes, bacteria for instance, and a few eukaryotes that have extrachromosomal DNA called plasmids. Plasmids are self-replicating genetic material.
It may be helpful to think of DNA molecules as individual instructions that our body uses to make proteins, and molecules essential for our growth, development, and health.
Thanks for watching this video over DNA. Until next time!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What does DNA stand for?
A
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
Q
What is DNA?
A
DNA is the genetic material of all living organisms with specific instructions for producing proteins.
Q
Who discovered DNA?
A
Friedrich Miescher was the first scientist to discover DNA in 1869. However, with the help of Rosalind Franklin, James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the double-helix shape of DNA in 1953.
Q
What is the function of DNA?
A
DNA contains the genetic blueprint and instructions for making proteins for the cell. This biological information can be inherited by offspring.
Q
What is the shape of DNA?
A
Double-stranded DNA consists of two complementary strands that adopt the shape of a double helix, which resembles a twisted ladder. 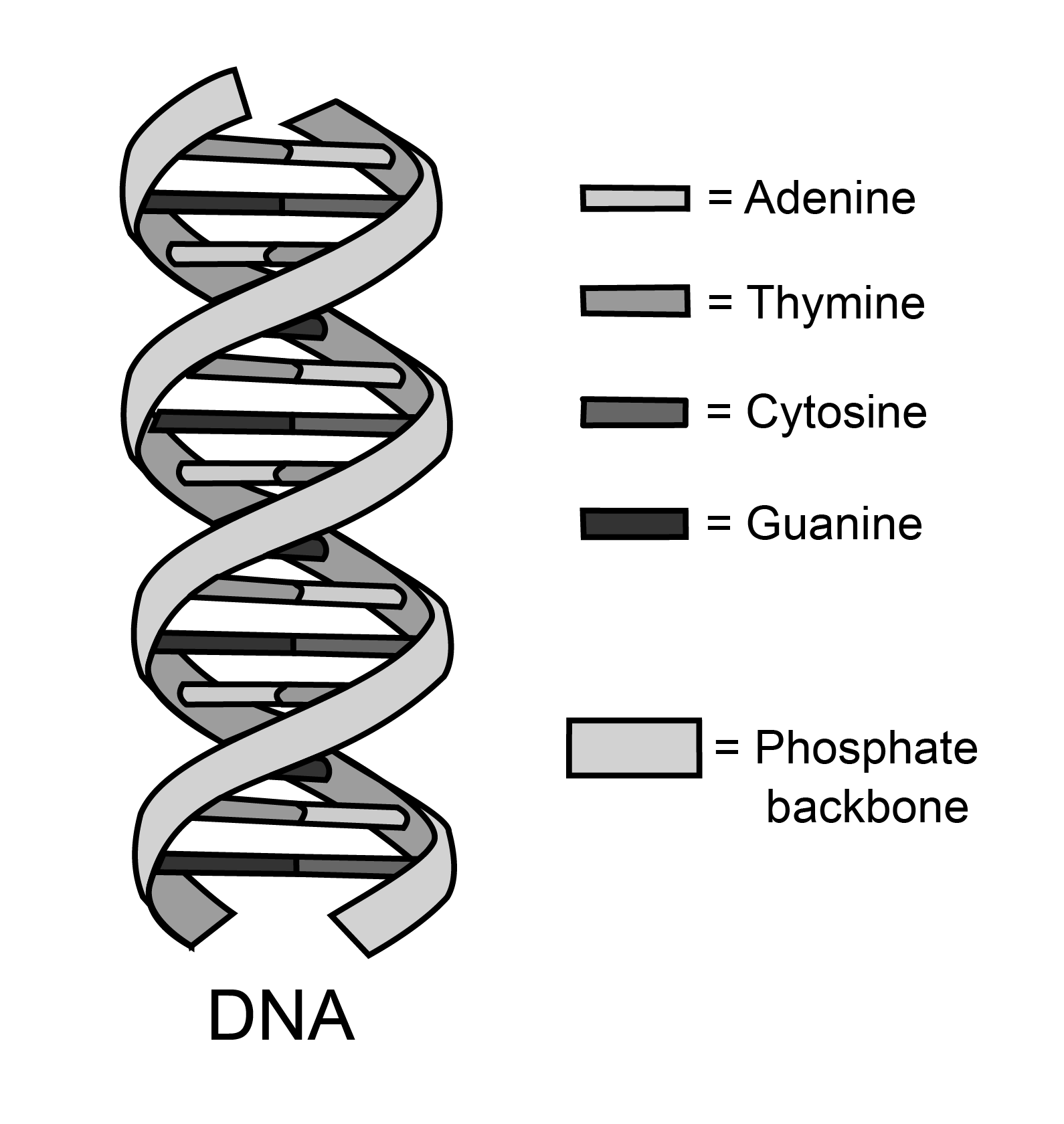
Q
Where is DNA found?
A
Majority of an organism’s DNA is found in the nucleus. However, a small amount can be found in the mitochondria.
Q
Do twins have the same DNA?
A
Fraternal twins have different DNA, while identical (maternal) twins have have the same exact DNA; however, new research may suggest it might not be perfectly identical.
