Hi, and welcome to this video on dilation!
What is Dilation?
Dilation is one of the main geometric transformations, along with translation, reflection, and rotation. Dilation is the scaling of an object, where it gets bigger or smaller. It’s what Ant-Man does in the Marvel movies! He stays the same shape but his size changes. Let’s get into how dilation works and how you can practice dilating shapes on your own!
Scale Factor
The number that determines the size change of an object is the scale factor. When we see a scale factor of exactly one, then the new object will be the exact same size as the original. When the scale factor is less than one, the new object will be smaller. For instance, a scale factor of 0.5 would result in the new object being half the size of the original. A scale factor greater than one results in the new object being larger than the original. So, a scale factor of 2.0 would result in the new object being twice the size of the original.
Dilation Examples
Example #1
Let’s try a dilation on a simple polygon—a rectangle:
We’ll use a scale factor of 0.4, which should result in a smaller rectangle. Our first step is to multiply the length of each side by the scale factor. Let’s start with the top and bottom by multiplying 24 centimeters times 0.4, which equals 9.6 cm. Now we’ll do the sides by multiplying 10 cm by 0.4 to get 4 cm. Now we can draw our new rectangle:
As you can see, we have a much smaller rectangle since the scale factor was less than one!
Example #2
Let’s try another one, but with a scale factor greater than one and use a triangle instead of a rectangle. We’ll also place it on the coordinate plane.
For our triangle, we’ll use a scale factor of 2, so the end product will be a larger triangle.
We’ll start by labeling the three vertices of the triangle. Let’s call our triangle “triangle ABC” and label the vertices A, B, and C. Then we’ll identify the position of each point on the coordinate plane.
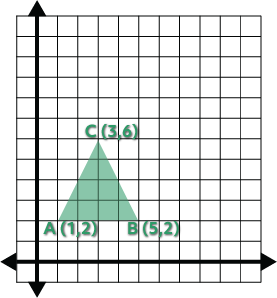
Now that we have three points, we can apply the scale factor of 2 to the \(x\) and \(y\) of each point. We do this by simply multiplying every \(x\) and \(y\) of each point by the scale factor. Since our scale factor is 2, that means we’ll double the values to create our new points.
Point A is located at \((1,2)\) so it has an \(x\) of 1 and a \(y\) of 2. If I multiply the \(x\) by 2, I get 2, and if I multiply the \(y\) by 2, I get 4. This new point is at \((2,4)\) and we’re going to call it A’. Let’s do the same thing for point B. We multiply the \(x\) of 5 by 2 and get 10 and the \(y\) of 2 and get 4. So our point B’ is at \((10,4)\). One more point to go! Point C has an \(x\) of 3, which when we double it is 6. It has a \(y\) of 6 which yields a value of 12 when we multiply by 2. So C’ is at \((6,12)\).
Once we have our three new prime points, we can plot them to create Triangle A’B’C’. It should be twice as big as our original triangle.
We can double-check by the lengths of the bottom side. On the original triangle, it’s four units wide, and on the new “prime” one it’s eight units wide. Success!
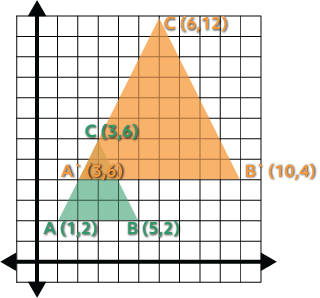
Example #3
Ready to try one? Pause this video and scale this quadrilateral by a factor of .5, which should make it smaller. Once you’re done, play the video to see if your new quadrilateral looks right.
Okay, here’s what you should have come up with:
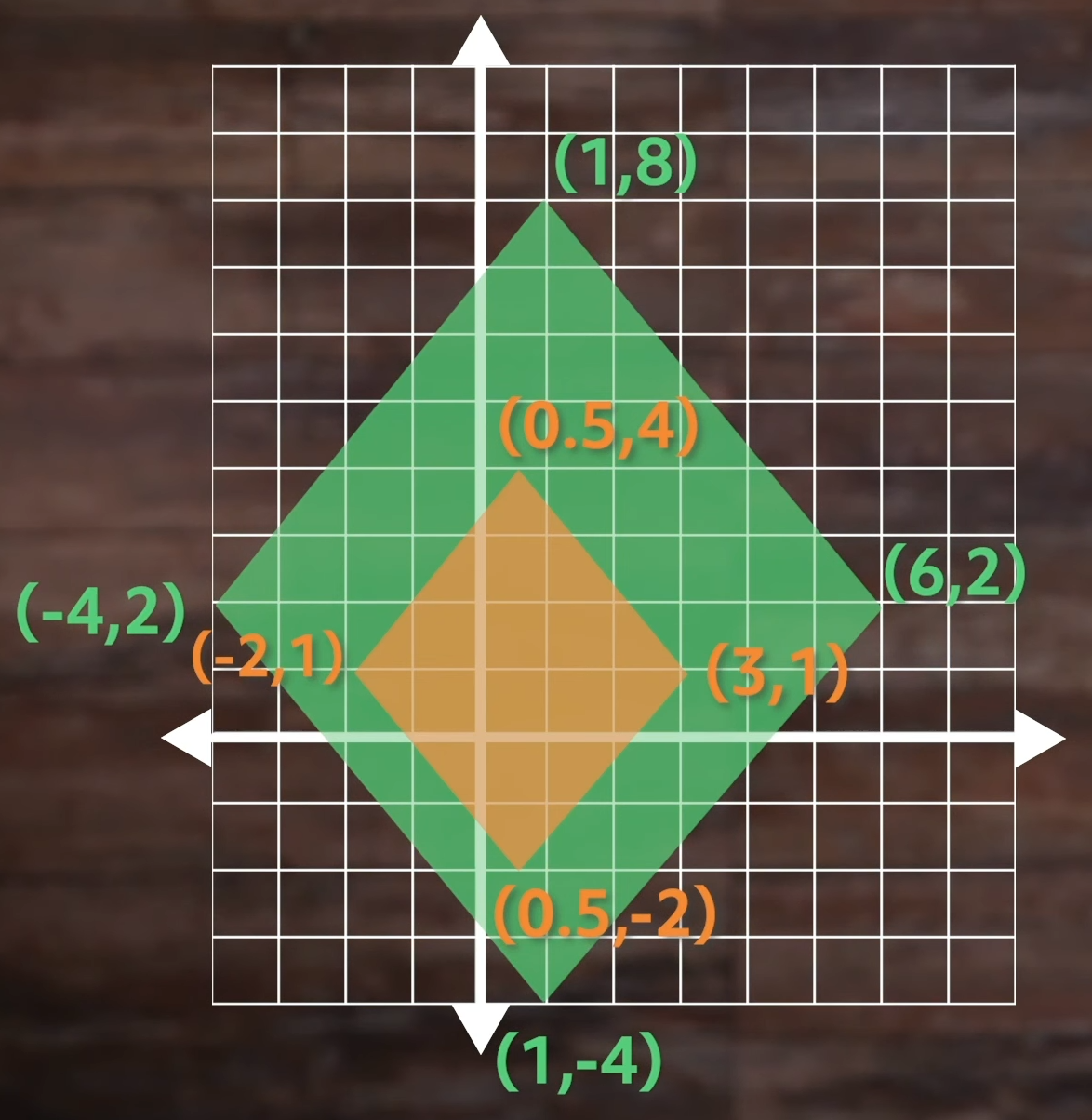
As you can see, we just cut each of our \(x\) values and \(y\) values in half by multiplying our values by our scale factor, 0.5.
I hope this review was helpful! Thanks for watching, and happy studying!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What is dilation in math?
A
Dilation is a process used to change the size of a shape to become either larger or smaller. Unlike other transformations, dilation often does not cause the shape to flip, rotate, or change position on the \(xy\)-plane. The only time dilation does cause a rotation is if it is multiplied by a negative scale factor. When this happens, the shape becomes larger or smaller and rotates \(180°\) about the origin. Dilation also does not cause the shape to become more narrow or thicker; it keeps the proportions of shapes the same and changes only their size. This is because all dilations have an associated scale factor, called \(k\), which describes to what degree the size of the shape will change. For example, if \(k=\frac{1}{2}\), the shape will shrink to half its original size, but if \(k=4\), the shape will grow to \(4\) times its original size.
Q
What is dilation of a triangle?
A
Dilating a triangle, as with any shape, will cause it to grow or shrink in size. It will not cause the triangle to rotate, flip, or distort. When \(k>1\), the triangle will grow as each of the \(3\) points of the triangle move away from the origin. On the other hand, when \(0<k<1\), the triangle will shrink as all \(3\) points move toward the origin.
Q
How do you dilate?
A
Two things are needed to dilate: an original shape and a scale factor \(k\). Write down the coordinates of each point of the original shape and label them. To find the points of the new, dilated shape, simply multiply each of the original coordinates by \(k\), then connect the dots!
For example, the corners of the red polygon ABCD have the following coordinates:
\(A:(-4,4)\)
\(B:(0,-2)\)
\(C:(4,0)\)
\(D:(8,4)\)
To dilate polygon ABCD with scale factor \(k=\frac{1}{2}\), we multiply each of the points’ \(x\)– and \(y\)-coordinates by \(\frac{1}{2}\). These new points will be called A’, B’, C’, and D’.
\(A’:(-4\times \frac{1}{2},4\times \frac{1}{2})=(-2,2)\)
\(B’:(0\times \frac{1}{2},-2\times \frac{1}{2})=(0,-1)\)
\(C’:(4\times \frac{1}{2},0\times \frac{1}{2})=(2,0)\)
\(D’:(8\times \frac{1}{2},4\times \frac{1}{2})=(4,2)\)
Q
Does dilated mean bigger or smaller?
A
A dilated shape can be bigger or smaller, depending on the scale factor \(k\). When \(k>1\), the shape will grow as all of its points move away from the origin. On the other hand, when \(0<k<1\), the shape will shrink as its points move toward the origin.
Q
What happens if you dilate a figure by a negative scale factor?
A
Even if the scale factor \(k\) is negative, the same rule applies: the coordinates of dilated points can be found by multiplying the original coordinates by \(k\). For example, the red triangle below has corners at points \((-1,-2),(2,2),\) and \((3,0)\). The green triangle is its dilation with \(K=-1\), so the dilated corners are at points \((1,2),(-2,-2),\) and \((-3,0)\), which can all be found by multiplying the coordinates of the original points by \(-1\).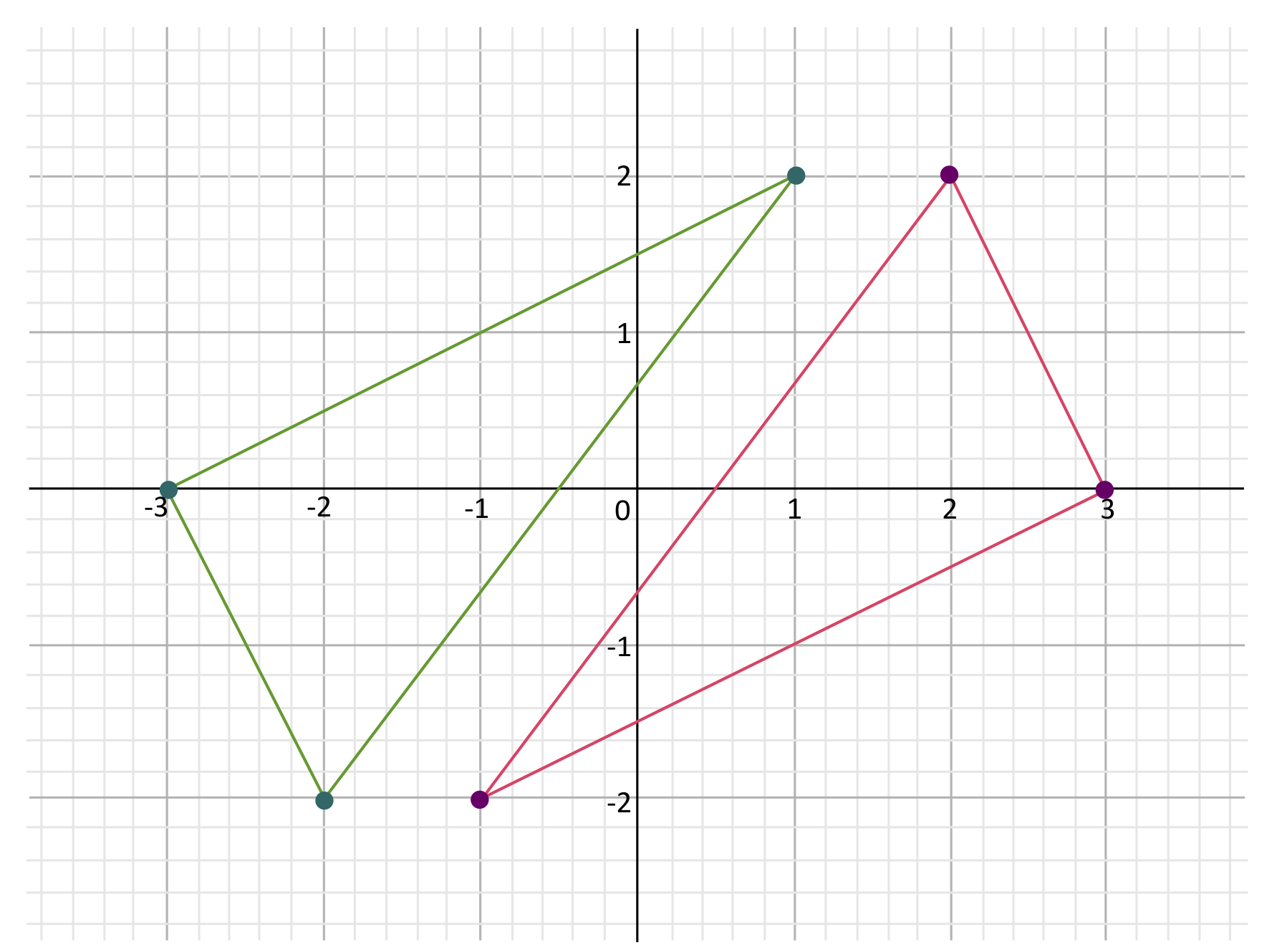
Sometimes it can be helpful to draw lines that connect the original points to the origin, and then follow those lines the appropriate distance past the origin to mark the dilated points.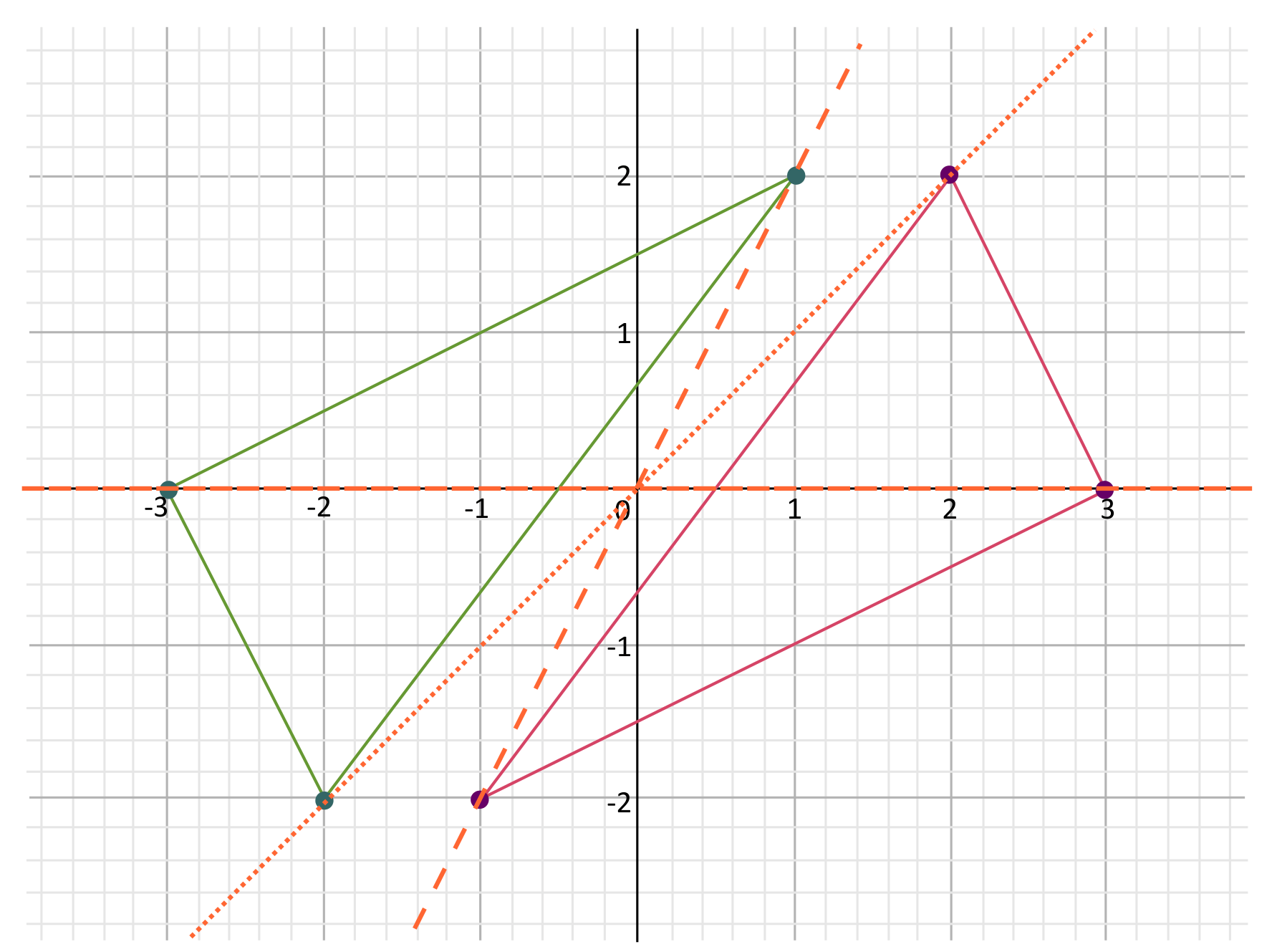
Notice that when you dilate by a negative scale factor, the figure is rotated \(180°\) about the origin.
Q
What stays the same in a dilation?
A
Because the coordinates of dilated points are all multiplied by the same \(k\), the proportions of the shape stay the same. For example, if done correctly, a square will not dilate into a long and skinny rectangle, and a trapezoid will not dilate into a rhombus.
Q
Does dilation change orientation?
A
Any time k is positive, orientation is not changed. The shape will still “face” the same direction. However, if \(k\) is negative, the dilated shape flips over across the origin, as shown below. This “flip” is the shape rotating by \(180°\) about the origin.
Q
Does dilation preserve distance?
A
No, dilation does not preserve distance. Because each point changes during dilation, and they all get closer to or further away from the origin, they also get closer to or further away from each other based on the scale factor.
Q
What’s the scale factor of dilation?
A
The scale factor of dilation is the degree to which a shape is grown or shrunk, and is denoted \(k\). When \(k>1\), the shape will grow as all of its points move away from the origin. On the other hand, when \(0<k<1\), the shape will shrink as its points move toward the origin. If \(k\) were to equal \(1\), then the shape would not change at all. If \(k\) were to equal \(0\), then all points would go straight to \(0\) and the shape would disappear. These relationships come from the fact that the coordinates of dilated points are the product of the original coordinates multiplied by \(k\).
\(A=(x,y)\) implies \(A’=(K\times x,K\times y)\)
Q
What is center of dilation?
A
The center of dilation is a fixed point on the plane that is the point of reference for where the shape may shrink towards or grow away from. It is most common for the center of dilation to be the origin, but it may be at other places on the plane. For example, the illustration below shows a dilation of a triangle from a center at \((-4,-9)\).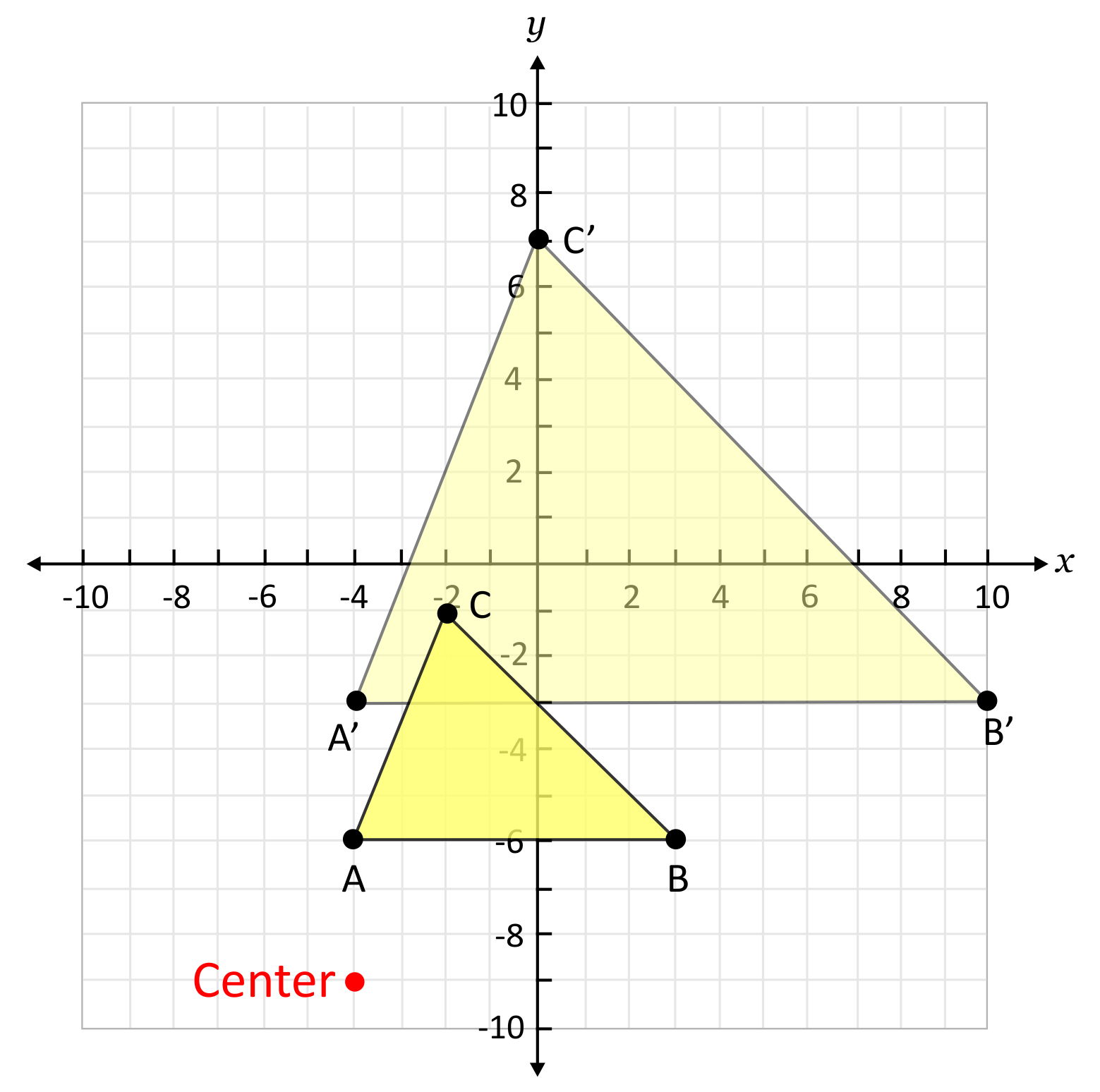
Geometry Dilation Practice Problems
Which of the following scale factors will cause the figure to become larger?
The correct answer is 2. In order for a scale factor to increase the size of an image, it must be greater than 1.
A triangle has vertices located at the points (-7, 2), (3, 1), and (4, 12). If the triangle is dilated by a scale factor of 3, which of the following is not one of the new points?
The correct answer is (6, 2). To dilate a figure by a scale factor, multiply both the x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of each point by the scale factor.
The new points are (-21, 6), (9, 3), and (12, 36).
A triangle has vertices at the points (8, -2), (12, -20), and (20, 16). If the triangle is dilated by a scale factor of \(\frac{1}{2}\), which of the following is not one of the new points?
The correct answer is (3, -5). To dilate a figure by a scale factor, multiply both the x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of each point by the scale factor.
The new points are (4, -1), (6, -10), and (10, 8).
Which of the following statements is true about a rectangle that is dilated by a scale factor of 2?
The correct answer is the area will be four times as large. When dilating a rectangle by a scale factor of 2, the length and width will both be doubled. This means that the area will be four (2×2=4) times as large, since the area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length by its width.
A triangle has vertices at the points (-3, -5), (4, 7), and (8, 11). If the triangle is dilated by a scale factor of 7, which of the following is not one of the new points?
The correct answer is (32, 44). To dilate a figure by a scale factor, multiply both the x-coordinate and the y-coordinate of each point by the scale factor.
The new points are (-21, -35), (28, 49), and (56, 77).