Imagine two friends, Alex and Jamie, discussing Jamie’s recent thrift store find. Jamie says, “This jacket was surprisingly inexpensive!” Alex replies, “I mean, it looked pretty cheap to me.”
This simple exchange captures the essence of connotation and denotation in our daily lives. While both words refer to the jacket’s low cost, “cheap” hints at poor quality, whereas “inexpensive” suggests a smart purchase. Today, we’ll explore how understanding these concepts can deepen our connections and enrich our conversations.
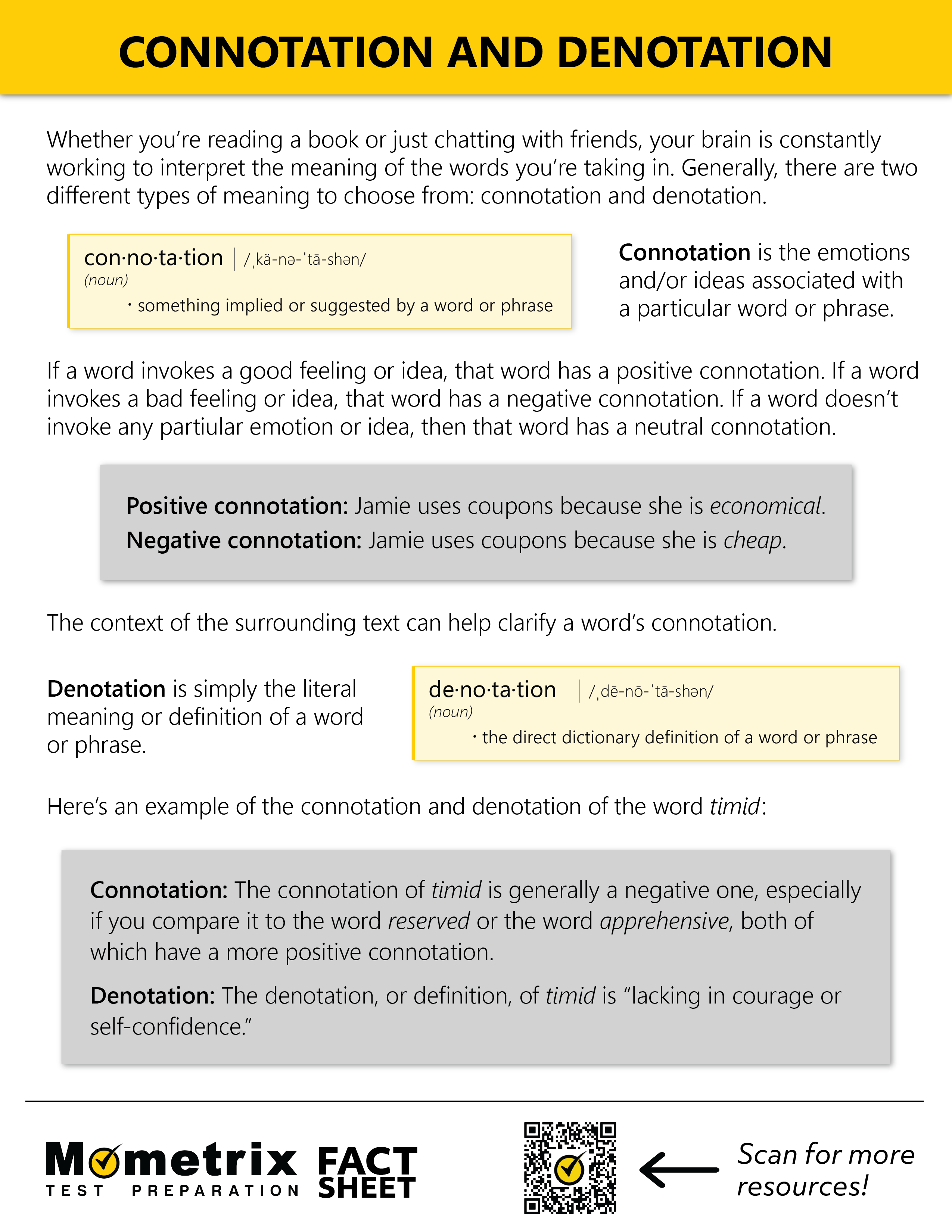
Connotation vs. Denotation
So what do the terms “connotation” and “denotation” actually mean? Denotation is simply the dictionary definition of a word. Connotation, however, is what emotions and/or ideas are associated with a particular word or phrase.
The way connotation and denotation work together in language helps us use words more effectively. It lets poets create vivid images, marketers persuade with their messages, and politicians inspire or provoke.
Connotation and Denotation Examples
Consider the word “youth.” Its denotation is simple: a period of life. Yet, its connotations can evoke vitality, naivety, or even rebellion. These layers of meaning, these connotations, are shaped by our experiences, our culture, and the context in which words are used. They color our perceptions and influence our reactions, often without our conscious awareness.
Words can have extremely different connotations, even when their denotations are similar. Let’s take “Curious” and “nosy,” for instance. The denotation of each word is similar, referring to the desire for knowledge. However, “nosy” often carries a negative connotation, suggesting an intrusive interest in others’ affairs.
For example, “Her nosy coworker wouldn’t stop asking about her weekend plans.” “Curious,” on the other hand, has a generally positive connotation, implying a more innocent eagerness to learn. For example, “He was curious about the new exhibit at the museum.”
As you can see, it’s not just about selecting the right words but also grasping their deeper impact on people’s feelings and thoughts.
Review
Before we wrap up, let’s go over a couple of practice questions.
1. “The company’s strategy was described as aggressive.”
Is the connotation of “aggressive” positive or negative in this context?
In this context, the connotation of the word “aggressive” is negative.
2. “Her approach to problem-solving was termed ‘innovative.’”
Is the connotation of “innovative” positive or negative in this context?
In this context, the connotation of the word “innovative” is positive.
3. “The policy changes were labeled as ‘strong’ by the committee.”
Is the connotation of “strong” positive or negative in this context?
This is actually an example where more context is needed to determine the connotation of a word. “Strong” could imply effectiveness in a positive sense, or excessive force in a negative sense, depending on further context.
4. “The restaurant’s ambiance was cozy.
Is the connotation of “cozy” positive or negative in this context?
In this context, the connotation of the word “cozy” is positive.
All right, that’s all for this review. Thanks for watching and happy studying!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What is connotation?
A
Connotation is the idea or feeling that a word invokes by adding to the literal meaning of the actual word itself. In other words, if a word has a “good” connotation, it is a word that invokes a positive feeling or idea; if a word has a “bad” connotation, it is a word that invokes a negative feeling or idea. The context of the surrounding text can help clarify the connotation of a particular word or phrase.
Good connotation: “Oscar uses coupons at the grocery store because he is economical.”
Bad connotation: “Oscar uses coupons at the grocery store because he is cheap.”
Q
What is denotation?
A
Denotations are the most literal meaning of a word or feeling; it is essentially the definition you would find in a dictionary.
Q
What is the difference between connotation and denotation?
A
Connotation is an indirect expression representing an implied feeling or meaning of a word, while denotation is the most literal meaning of any given word. For example, the denotation of the word timid is “lacking in courage or self confidence.” The connotation of timid is generally a negative one, particularly if you compare it to the word reserved or the word apprehensive, which have a more positive connotation.
Q
What is a negative connotation?
A
Negative connotations are bad feelings or emotions that affect people when they hear certain words or phrases. Negative connotations can drastically affect or change the meaning of the text.
For example, when comparing the words elderly and mature, the word with a negative connotation would be elderly. While mature invokes the idea of dignity and wisdom, elderly invokes the idea of an older and perhaps weaker person.
Q
What is a positive connotation?
A
Positive connotations are words that create happy feelings and moods within a text, contrasting the negative connotations that cause negative feelings.
For example, when comparing the words curious and nosy, the word with a positive connotation would be curious. While nosy invokes the idea of someone prying into other people’s business, curious invokes the idea of someone desiring to learn about something new.