
What is Syntax?
Syntax is the law of language that determines the word order and basic sentence structure within the different languages.
Each language has a specific syntax that tells the speaker and the listener which parts of the sentence come first to help them make sense of what’s being said. It’s the guidelines we use when speaking and writing so that sentences are understandable and coherent.
Be wary of confusing syntax or semantics with diction. These form the backbone of sentence construction, so let’s break these definitions down.
- Syntax, as just mentioned, is the order of the words in a sentence.
- Diction is the specific word choice meant to express certain meanings.
- Semantics is the meaning conveyed by the particular words used.
We’ll be focusing on syntax for this video. In the English language, there is a word order that is set in stone for most types of sentences. Of course, there are always exceptions, but most of the time, standard English sentences will follow an SVO word order.
- Subject
- Verb
- Object
Syntax Examples
In this example sentence, we have the subject boy, the verb looks, and the object outside.
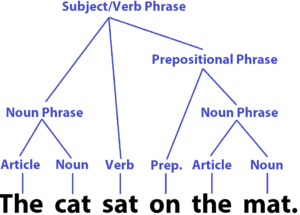
The image above is of an English grammar syntax tree used by linguists to plot the structure of sentences. You may not often encounter a syntax tree, but knowing how to draw one is rather useful and will help you understand sentence structure.
In the chart, you can see that the sentence is broken down into its parts: verbs, nouns, articles, and prepositions. After this step, the words are grouped together to determine which parts of the sentence are noun phrases, prepositional phrases, or verb phrases.
Fun fact: SVO is not the only word order structure. Other languages vary word order and even include additional components in their syntax.
In the example given with the syntax tree, the subject is cat, the verb is sat, and the object is mat.
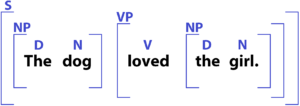
This second picture is another way in which syntax can be written out. This diagram takes the sentence “The dog loved the girl” and breaks it down into articles (D), nouns (N), verbs (V), noun phrases (NP), and verb phrases (VP) just like the previous example. In this sentence, the subject is dog, the verb is loved, and the object is girl.
Again, the syntax trees are not to be intimidating but are used to better understand the structure of a sentence and to reveal each part’s purpose within the sentence.
An additional use for syntax trees is that whenever a different word order is used for a sentence, it can be “decoded” by charting it out like the examples above. For example, if you are hearing a sentence in a foreign language that follows a VSO order or some other variation, creating a syntax tree for that sentence can help you to put the words in SVO order so that you might understand what’s being said.
Review
Let’s have a recap!
- Syntax is the sentence structure.
- Diction is the choosing of words to relate a certain meaning.
- Semantics is the meaning that is expressed from the words used.
- Syntax trees are a neat graphing tool to chart sentence structure and make sense of word order and how it’s functioning in the world of English.
Thanks for joining us on this syntax tutorial! See you next time!
