Hi, and welcome to this video on isotopes!
Let’s jump right in with a definition.
Isotope: various forms of the same element that have an equal number of protons (and therefore the same atomic number) but differing numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and therefore have different atomic mass but not chemical properties (a common example would be a radioactive form of an element).
As of now, all 81 elements have at least one isotopic form. There are currently 275 isotopes of the 81 stable elements, which does not include the over 800 unstable and radioactive isotopes.
Let’s take a look at some examples.
Example 1
Carbon atoms exist naturally with 6, 7, or 8 neutrons. Since each atom of carbon has 6 protons, the isotopes must have atomic masses of 12, 13, and 14. (Since atomic mass = mass protons + mass neutrons)
These isotopes are called carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. Alternatively, they may be written 12C, 13C, and 14C.
Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are stable. Carbon-14 is unstable, decaying with a half-life of about 5,700 years.
Example 2
Hydrogen is unique in that it’s the only element whose isotopes have alternative names. Let’s take a look:
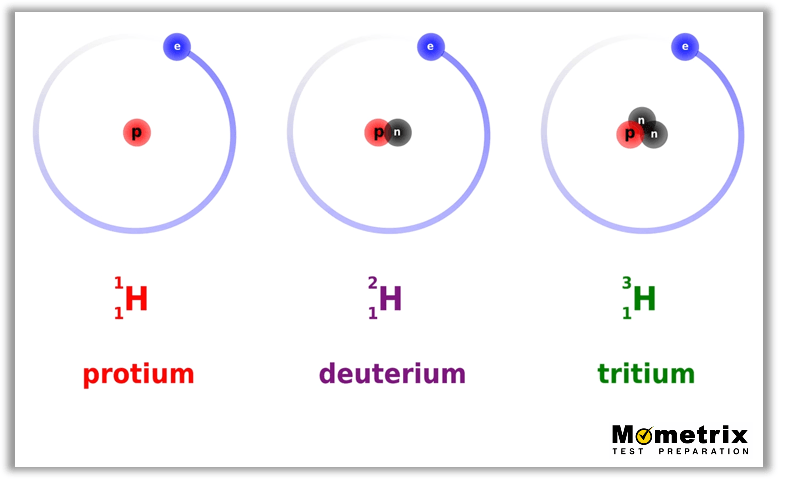
I hope that helps! Thanks for watching this video lesson, and until next time, happy studying!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q
What is an isotope?
A
Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons (same element) but a different number of neutrons (different atomic mass). Isotopes have all the same chemical properties and reactivities. Many elements have multiple naturally-occurring isotopes in various ratios. The mass and relative abundance of each isotope are factored together (as a weighted average) to find the atomic weight of an element.
Q
What is a radioactive isotope?
A
A radioactive isotope, or radioisotope, is an unstable isotope that releases excess energy and particles through the process of radioactive decay.
Q
How do you find isotopes?
A
Since all isotopes of a given element are chemically identical, there are no chemical methods of separation possible. The only methods currently utilized to separate isotopes rely on the minute differences in the mass of the atoms. This can be achieved in few different ways, but most commonly via diffusion, centrifugation, or distillation.
Q
How do you write isotopes?
A
Isotopes are identified in either hyphenated form (uranium-238) or in standard notation \((^{238}_{\phantom{0}92}\text{U})\). In both notations, the number of protons (92) and the neutrons (238 – 92 = 146) of the isotope is communicated, if somewhat hidden.